Over time, that new capital will be deployed and should drive higher profits and ROE. Hence, the investor needs to have looked upon both the book value or the book price of the company as well as the market price of the stock and then decide on the company’s worthiness. In banking, a strong TCE ratio is required to ensure that the bank can absorb losses and protect depositors. Regulators often require banks to maintain a minimum TCE ratio to ensure financial stability. Preferred stock typically has a fixed dividend rate, which means you know exactly how much you’ll get paid each year.
Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC)

It primarily includes the funds raised from issuing common stock and retained earnings, which are the accumulated profits not distributed as dividends. By evaluating common equity, investors can determine if a company is financially stable, helping them make informed decisions about whether to invest in its stock. The stockholder’s equity can be calculated by deducting the total liabilities from the company’s total assets. In other words, the Shareholder’s equity formula finds the net value of a business or the amount that the shareholders can claim if the company’s assets are liquidated, and its debts are repaid.
Example of Total Equity
Owning equity will also give shareholders the right to vote on corporate actions and elections for the board of directors. These equity ownership benefits promote shareholders‘ ongoing interest in the company. In the stock market, shareholders‘ equity (or owners‘ equity for privately held companies) represents the difference between a company’s assets and liabilities. If all of the company’s assets were https://image.kingteeshop.net/2024/10/16/our-services/ liquidated and used to pay off debts, the shareholders‘ equity is the amount that would be left over. In the case of an acquisition, it is the value of company sales minus any liabilities owed by the company that are not transferred with the sale. Tangible common equity is most often used when evaluating the position of financial companies like banks.
Difference from Preferred Equity
- Deriving the common equity is also the first step in obtaining further useful metrics such as Return on Common Equity, or ROCE.
- Of the 50.4 million shares authorized, the company had issued roughly 15.1 million shares.
- The “Treasury Stock” line item refers to shares previously issued by the company that were later repurchased in the open market or directly from shareholders.
- Often times, it is more important to a shareholder than return on investment (ROI).
- But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs due to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value.
In rare cases, a negative ROE ratio could be due to a cash flow-supported share buyback program and excellent management, but this is less likely to be the circumstance. In any case, a company with a negative ROE cannot be evaluated against other stocks with positive ROE ratios. A common scenario is when a company borrows large amounts of debt to buy back its own stock. This can inflate earnings per share (EPS), but it does not affect actual performance or growth rates. Whether an ROE is deemed good or bad will depend on what is normal among a stock’s peers.
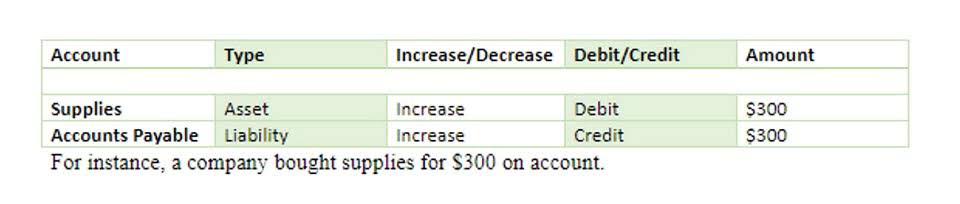
At times companies buy back some floating shares as part of corporate total common equity formula strategy. These repurchased shares are not canceled but rather held by the company as treasury shares in their books. Common Stock is the equity capital at the par value of the shares, and the additional paid-in capital is the excess capital over and above the par value.

Company equity is an essential metric when determining the return being generated versus the total amount invested by equity investors. For example, return on equity (ROE), which is the company’s net income divided by shareholders‘ equity, measures how well a company’s management is using equity from investors to generate profit. How to Run Payroll for Restaurants Common stock is a component of common equity, representing the shares issued to investors.
How Stockholders‘ Equity Works
- The fundamental accounting equation states that the total assets belonging to a company must always be equal to the sum of its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
- Generally, the owner’s equity of a company is influenced by the industry in which it operates and how well it can manage its assets and liabilities.
- Take the sum of all assets in the balance sheet and deduct the value of all liabilities.
- This is the same figure reported lower on the balance sheet, under shareholder equity.
- The ROCE ratio can also be used to evaluate how well the company’s management has utilized equity capital to generate values.
- With a low equity base, the company may be struggling with its debt levels, making it harder to secure loans or attract investors.
An outsize ROE can be indicative of a number of issues, such as inconsistent profits or excessive debt. In general, both negative and extremely high ROE levels should be considered worth investigating. Here you need to provide the four inputs Total Assets, Total liabilities, Preferred Stock, and Number of common shares. It is the portion of the company profit not paid off to the company’s shareholders in the form of dividends. It is accumulated over a while if the company performs well and forms part of the shareholder’s equity.
- A higher common equity ratio indicates that the company has more assets than liabilities and that it relies less on debt financing.
- Projected Terms are based upon the anticipated redemption or maturity date of the corresponding project investment.
- We hope to provide a well-rounded, multi-faceted look at the past, present, the future of EdTech in the US and internationally.
- Stockholders‘ equity is a measurement of the general financial health of the company.
- A positive total equity figure indicates potential growth and profitability, while negative equity might signal financial distress.
- This metric reflects how effectively management uses equity financing to grow the business, making it an essential factor in investment decisions.
How to Spot Stock Market Trends: A Guide to Smart Investing
On the other hand, an investor might feel comfortable buying shares in a relatively weak business as long as the price they pay is sufficiently low relative to its equity. Private equity generally refers to such an evaluation of companies that are not publicly traded. The accounting equation still applies, where stated equity on the balance sheet is what is left over when subtracting liabilities from assets, arriving at an estimate of book value.

Sometimes, a venture capitalist will take a seat on the board of directors for its portfolio companies, ensuring an active role in guiding the company. Venture capitalists look to hit big early on and exit investments within five to seven years. An LBO is one of the most common types of private equity financing and might occur as a company matures.